Sea salt and table salt might seem like the same basic ingredient, but there are several differences between these two types of salt. They differ in terms of both origin and nutrition and could change the taste of some recipes.
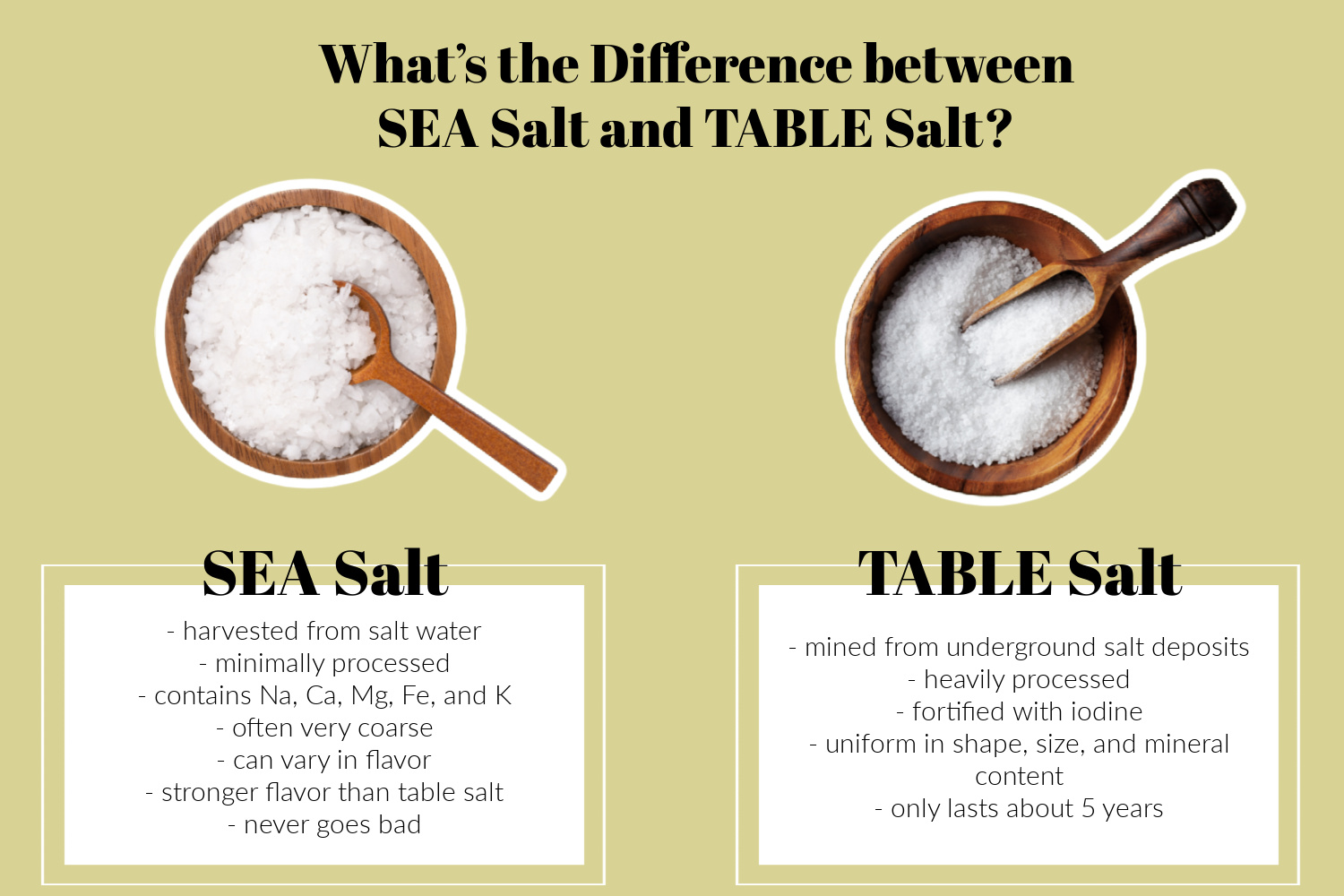
6 Differences Between Sea Salt and Table Salt
1. Origin
Table salt is mined from underground salt deposits, while sea salt is harvested by evaporating the water content in salt water.
2. Processing
Table salt is processed heavily after the mining process to remove impurities as well as some minerals. Because so much is removed during this processing, table salt is later fortified with iodine.
Sea salt, on the other hand, is minimally processed, maintaining its original mineral content, so it doesn’t need to be fortified prior to sale.
3. Mineral Content
During the fortification process, Iodine is added to table salt, which is a necessary mineral in the human diet. Beyond this, there isn’t much mineral content in table salt beyond sodium.
Sea salt contains sodium, calcium, magnesium, iron, and potassium, but it small and varying amounts. While this does make sea salt slightly healthier, it does not contain the necessary nutrient iodine.
4. Shape/Size
Table salt is uniform in shape, size, and mineral content, while sea salt can vary based on the saltwater it is derived from. Sea salt is often very coarse and needs to be put in a grinder prior to use.
5. Flavor
Sea salt, because of the minimal processing, can vary in flavor, but it tends to retain a stronger flavor than table salt, making it ideal for recipes where the salt flavor needs to come through (such as in sea-salted caramel).
6. Shelf Life
Table salt only lasts about 5 years because the additives added during processing begin to decay. Sea salt, on the other hand, can last almost forever and never goes bad.
Is Sea Salt Healthier Than Table Salt?
Although these sea salt and table salt vary in shape, flavor, and mineral composition, they have the same health benefits. While you might get a wider variety of minerals from sea salt, the amount varies so widely that it can’t be counted as an actual source of these minerals. Additionally, table salt contains iodine which is a nutrient that is essential to thyroid function—something which sea salt doesn’t have.
Can You Use Sea Salt and Table Salt Interchangeably?
Sea salt and table salt should not be used interchangeably. Sea salt has a stronger salt taste, which can disrupt the flavor of baked goods and other delicate recipes.
Unless a recipe calls for sea salt, table salt should always be used prior to or during the cooking process. Whereas, sea salt should be saved for a finishing touch or when serving the final product.
Leave a Reply