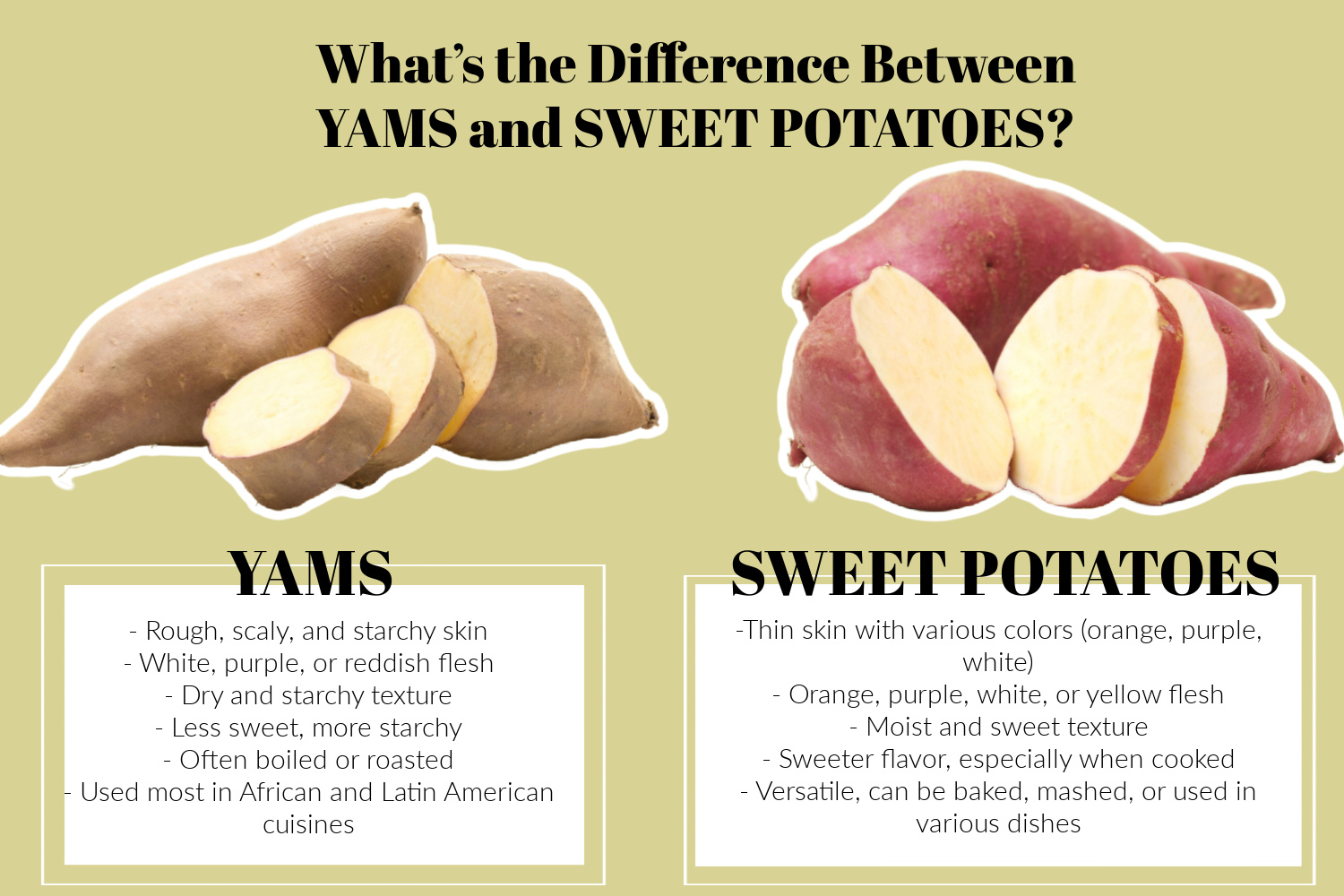
It’s common to think that yams and sweet potatoes are the same vegetable, but they are actually different from one another. While both yams and sweet potatoes look alike, they differ in size, availability, and taste.
6 Differences Between Yams and Sweet Potatoes
1. Size
Yams are larger than sweet potatoes, though they can come in all sizes. Sweet potatoes don’t grow nearly as large as yams do.
2. Color
Only yams are bright in color, usually orange, red, or purple on the inside. Sweet potatoes have a less vibrant color and tend to have white or yellow inside flesh, though lighter orange flesh can sometimes be seen, which is why people confuse the two.
3. Taste
Sweet potatoes are known for being much sweeter than yams, and yams are much more starchy than sweet potatoes.
4. Consistency
Yams are much softer and more moist than sweet potatoes, making them easier to open and enjoy.
5. Origin
Yams are actually a modified stem, rather than a root (as sweet potatoes are) putting them in the vine family. Yams are closer to lilies than they are to sweet potatoes, and they only grow in tropical regions like Africa and the Caribbean.
Sweet potatoes grow in colder, drier climates, like North America, though they can be found in South America as well. Though some of the larger sweet potato varieties in the United States can be labeled as yams, they are usually sweet potatoes and just labeled as yams for marketing purposes.
6. Vitamin Content
Yams are high in starch and contain fiber, Vitamin C, potassium, magnesium, and some Vitamin B6. Sweet potatoes have all these same vitamins, but they also contain Vitamin A, beta carotene, and some sugar, making them slightly less healthy than yams.
Should You Cook Yams or Sweet Potatoes?
In North America, you likely won’t be able to buy real yams in the store, as usually only sweet potatoes are sold. Regardless, sweet potatoes are usually tastier and the ones that should be used to make any casserole or roasting recipe.
Leave a Reply